IAUGT Class
Biblical Guide to Interpreting and Understanding the Word of God - Part 1
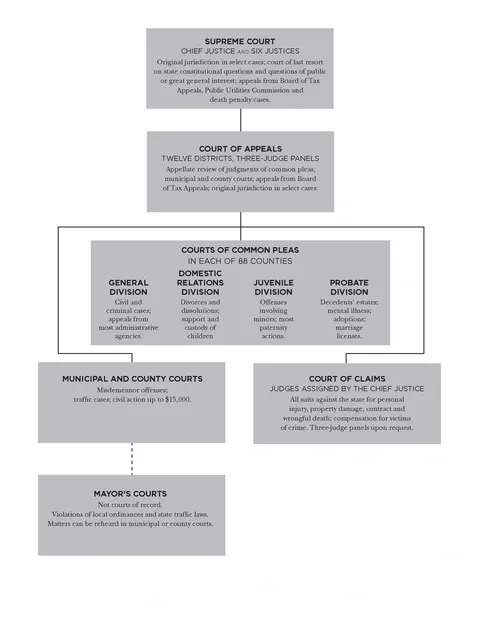
Structure of the Ohio Judicial System
Ohio Judicial Structure
The Constitution of Ohio separates our state government into three branches, each with distinct areas of responsibility — the executive, the legislative and the judicial.
The primary function of the judicial branch is to fairly and impartially settle disputes according to the law. To do this, a number of courts have been established in the state by the Constitution and by acts of the General Assembly.
Further, in addition to its place in the court structure as the court of last resort, the Supreme Court, in particular the Chief Justice, is responsible for the administration of the judicial branch in Ohio.
The Supreme Court of Ohio
The Supreme Court of Ohio is established by Article IV, Section 1, of the Ohio Constitution, which provides that “the judicial power of the state is vested in a Supreme Court, Courts of Appeals, Courts of Common Pleas and divisions thereof, and such other courts inferior to the Supreme Court as may from time to time be established by law.â€
Dayton & Montgomery County Criminal Justice System
The Dayton Municipal Court was created in 1913 by the Ohio State Legislature and began its judicial operation in 1914. The court has boundaries of the City of Dayton. The court has subject matter jurisdiction over a violation of any ordinance of the City of Dayton; any state of Ohio statutory misdemeanor or traffic violation committed in Dayton; and jurisdiction to preside over preliminary hearings for felony cases that occur in the City of Dayton. Jurisdiction also includes civil cases when the amount in dispute is $15,000 or less and for small claims cases when the amount in dispute is $6,000 or less.
The General Division of the Montgomery County Common Pleas Court is a trial court of general jurisdiction that provides prompt, fair and just resolution of litigation in civil and criminal cases.


Montgomery County Common Pleas Court
There are sixteen Judges in the Common Pleas Court for Montgomery County. The Judges are elected to and conduct their work in one of the four divisions. In some instances, the Presiding Judge will assign a Judge from one division to another for specific cases. This is done to avoid the cost and delay involved with a Judge from another county being assigned to a matter.
The General Division has eleven Judges responsible for civil cases and criminal felony cases. One is African American and ten are Caucasian. Eight are male and three are female. The Honorable Judge E. Gerald Parker Jr. is the first and only African American male judge in the Montgomery County Common Pleas Court, General Division. Civil cases involve disputes between parties for such things as unpaid debts, personal injuries from accidents, contract disputes and other conflicts arising out of different types of business transactions. Criminal felony cases are prosecutions for crimes that can result in a prison sentence for the offender. Felony cases are divided by classifications from One to Five with Level One crimes being the most serious offenses.
The Domestic Relations Division has two Judges empowered by statute to hear all divorce, dissolution, legal separation, and annulment cases, as well as civil domestic violence cases for residents of Montgomery County. One is African American and one is Caucasian. One is male and one is female. In addition, the Court maintains jurisdiction over post-decree matters such as allocation of parental rights and responsibilities, child support, parenting time issues, spousal support, and other related matters.
The Juvenile Division has two Judges with jurisdiction over cases regarding delinquent and unruly children, as well as those youth charged with traffic violations. Both are Caucasian. One is male and one is female. The Court also makes judicial determinations relating to dependency, neglect, abuse, paternity, child support, and parenting time.
The Probate Division has one Judge with exclusive jurisdiction over the administration of estates and trusts, appointment of guardians for incompetents and estates of minors, adoptions, the issuance of marriage licenses, name changes, commitment of the mentally ill, and various other actions. The judge of this court is African American and female. The Court also approves settlements in wrongful death actions and minor injury claims. The Probate Division is empowered with more than two hundred responsibilities pursuant to the Ohio Revised Code.
Dayton Municipal Court Judges
Five full-time judges serve on the Dayton Municipal Court. Four are African American and one is Caucasian. Three are male and two are female. Each judge is elected on a nonpartisan ballot to serve a six-year term of office. Judges must be attorneys, required to have practiced law for a minimum of six years and be residents of the City of Dayton. All judges are sworn to administer justice in every case and to ensure that the cases before them are conducted in an impartial and equitable manner. Annually, the judges elect a Presiding Judge and an Administrative Judge. These judges meet regularly with the Court Administrator to review the operations and policies of the court.
Two full-time magistrates are appointed by the court to hear certain civil cases, small claims cases, eviction procedures and initial appearances for defendants summoned in for arraignment. They also preside over minor traffic and criminal cases.
The administrative, professional, technical and clerical functions of the court are provided by 55 court employees. Support positions include a court administrator, magistrates, legal assistant, court technology manager and IT technical support coordinator, probation officers, assignment coordinators, bailiffs, marshal, secretaries , paralegals, and electronic home detention officers.





